mobile computing
What is mobile computing?
Mobile computing refers to the set of IT technologies, products, services and operational strategies and procedures that enable end users to access computation, information and related resources and capabilities while mobile. Mobile most commonly refers to access in motion, where the user is not restricted to a given geographic location.
Mobile may also refer to access in a fixed location via equipment that users can relocate as required but is stationary while in operation. This mode of operation is often called nomadic computing.
Today, mobile computing technology is everywhere. It has applications in business and consumer markets, industrial and entertainment industries, as well as many specialized vertical markets.
Desktop computers offer more hardware configuration capabilities and computational performance. However, the majority of end users prefer mobile devices. The key advantage of mobile computing is convenience, where users have access to information and computational resources anytime and anywhere.
How does mobile computing work?
Generally, a mobile computing system involves a mobile device, such as a laptop computer, tablet or smartphone, and a wireless network connection based on Wi-Fi or cellular wireless technology, such as 5G. Mobile devices typically can store data locally, and access to that data doesn't require a network connection.
Mobile computers typically accommodate access to both wireless and wired technology. Access to shared network resources, including Mobile cloud-based resources, is essential given the collaborative nature of work today. Integrated, rechargeable batteries power mobile devices, and most can run on an alternating current (AC) power source when used from a fixed location.
In addition to laptops, tablets and smartphones, there are many mobile computing devices for vertical and specialized applications. These include devices for medical, surveillance, security, and telemetry and control uses.
Device selection is based on the application. For example, laptops are better suited for content creation, and tablets are often preferred for content consumption. Smartphones function as pocket-size computers and communication devices, but they have small screen sizes and screen-based keyboards.
Why is mobile computing used?
Mobile computing is used in most facets of life both in business and by consumers. It enables users to be untethered from a power source for periods of time. This is advantageous for traveling workers who want to stay connected to their work while on the move. It's also useful for remote workers who may not have all the connectivity and power options they have in an office setting.
Consumers use mobile computing in several ways, including the following:
- internet access
- mobile communications
- web browsing
- mobile applications
- entertainment streaming media
Mobile devices and apps can collect user data in various environments and contexts. Fitbits and smartwatches are examples of wearable technology that collect user data in novel contexts, including fitness and health settings.
Mobile computing also makes the internet of things (IoT) possible. The nontraditional computers, sensors and other devices that make up IoT are able to connect and communicate without direct human intervention.
What are the types of mobile computing?
Mobile computing is a combination of infrastructure, hardware and software technology. The various parts of mobile computing are as follows:
- Mobile infrastructure. Infrastructure refers to the technical pieces that allow devices to communicate. Mobile infrastructure includes the wireless networks, wireless protocols and data formats.
- Mobile hardware. The physical mobile device and supporting hardware that users interact with make up the mobile hardware. This may include cell phones, laptops, tablets, wearable computers and accompanying chargers and accessories.
- Mobile software. This refers to the applications that run on mobile devices, including mobile operating systems (OSes) and user-facing applications, such as mobile browsers and e-commerce applications.
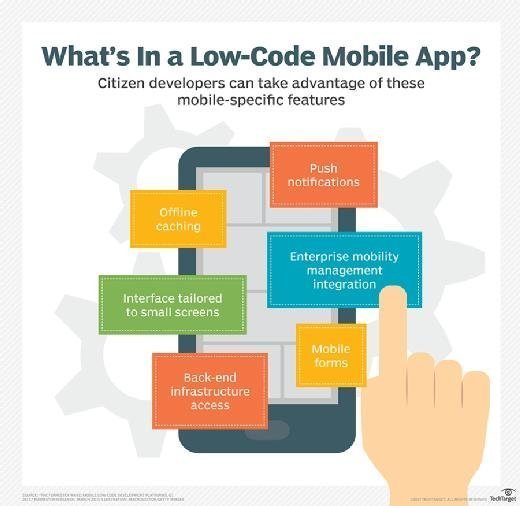
Some different types of mobile computing include the following examples:
- Consumer use. Consumers can use mobile devices like laptops, smartphones, wearables and tablets for an array of activities, including communication, entertainment, banking, bill paying and health and fitness tracking.
- Remote work. Employees use laptops or tablets to work and collaborate. Delivery personnel use mobile devices for logistical and management information, and to verify that deliveries were made to the right place. Field service technicians use mobile devices for field service management, tracking and support capabilities.
- IoT. Consumer and enterprise IoT devices are used to communicate with other devices without human intervention. For example, self-driving cars use sensors, onboard computers and other connected devices to connect with GPS, weather and other systems to navigate the road safely. Smart sensors are also used in supply chain management systems to track the progress of goods in transit.
Mobile technologies
Most microprocessor vendors offer mobile versions of their products. These products consume less power and are physically smaller than their desktop counterparts. Consequentially, they often don't perform as well as the desktop products. However, this is not an issue for most mobile applications because a range of products at various price points are available that address most application demands.
Today's Wi-Fi and 5G networks offer ultra-low latency throughput that supports most mobile applications. Unlimited cellular data plans make data costs manageable, offering good availability, reliability, throughput and bandwidth.
Color graphics displays are universal on mobile devices, and touch is the primary user interface. These displays consume a lot of battery power, which is why product engineers continue to improve backlighting for LCD screens and OLED displays.
Mobile devices today use a mix of cloud and local storage. They typically use solid-state storage designs based on flash memory technology instead of physically heavier and more fragile hard drives.
What are the advantages of mobile computing?
The advantages of mobile, ubiquitous computing include the following:
- Portability. Mobile devices are smaller and more portable than traditional computers, making them easy to carry and use in a range of contexts. They work disconnected from a power source and without a physical network connection and when disconnected from the network.
- Affordability. Over time, mobile devices have become less expensive and easier to obtain. Increasingly, people opt for smartphones and tablets as their primary means of online connectivity. And it is often cheaper to buy a smartphone than a desktop PC.
- Wireless communications. Mobile devices let users engage in phone, video and various text and instant messaging applications.
- Data. Mobile devices and applications enable companies to collect more consumer data than was possible with traditional computing. For example, mobile devices can record geolocation of the device and its user. A marketing company can use a behavioral analytics application to match the location of a device with the user's behavior on the device, and then target advertisements to the user at that given moment. This is a common practice in neuromarketing. Some mobile applications also collect biometric data, such as heart rate readings, which can help users track their health.
What are the limitations of mobile computing?
Mobile computing is not without issues such as the following ones:
- Power. Despite increasing battery life, power consumption continues to be an issue, and mobile devices must be recharged regularly.
- Connectivity. While the mobile infrastructure continues to improve, there are areas where signal strength is poor or nonexistent.
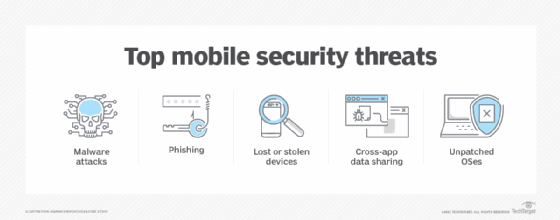
- Data security. Mobile computing raises significant data security vulnerabilities because business users, especially, may have sensitive data on their devices while traveling or working remotely. Companies must implement security measures and policies to keep corporate data secure.
- Dependence. The flip side to the convenience of mobile devices is that consumers may become overly reliant on them, which can lead to compulsive or unhealthy behaviors such as smartphone addiction.
- Distraction. Mobile devices can be distracting and potentially dangerous in a hazardous work environment that requires the employee's attention, such as a construction site. They pose dangers if used inappropriately while driving.
Evolution of mobile computing
In the early 1970s, mainframe computing sometimes provided remote access using a modem-based dial-up connection, typically at 300 to 1,200 bits per second (bps). Users worked teletype or cathode ray tube (CRT) terminals. Mobile terminals appeared during this era as well. These portable devices were larger, heavier and more expensive than today's mobile computers, and network speeds were slow.
The development of the first mobile computers in the late 1970s were on sewing machine-size PCs, such as the Osborne 1 and the Compaq Portable. These were based on early OSes, such as CP/M and MS-DOS. They used floppy disks, small monochrome CRT displays and, when available, plug-in (RJ-11) modems of up to 2,400 bps. These nomadic devices still required AC power, but they enabled portable computing.
Early laptop computers, such as the GRiD Systems Compass Computer 1101, also required AC power and were large, heavy and expensive. Laptops became popular in the 1990s as technology improved and design became more portable, especially as the smaller notebook form factor evolved. Add-on and internal Wi-Fi links, reliable battery power and contemporary OSes, such as Microsoft Windows, MacOS and Linux improved displays and reduced prices.
Personal digital assistants (PDAs), which first appeared in the early 1990s, were an outgrowth of personal organizer devices. These were designed to store and retrieve information needed for personal productivity, such as calendars and phone directories.
The first commercial mobile phone appeared in 1983. Phones gained popularity as they became more portable and networks became more ubiquitous. The addition of cellular voice, data and Wi-Fi led to the smartphone. Blackberry introduced the first smartphone in 2002, and the Apple iPhone's launch in 2007 opened the floodgates of user demand. Improvements in hardware components led to the development of mobile OSes; Apple iOS was introduced in 2007 and Android in 2008.
The tablet PC, featuring touchscreen and pen interfaces, is rooted in popular industrial and commercial applications of the 1980s. Apple released the first iPad in 2010. It introduced many consumers to this form factor, and both iOS and Android models remain popular today. Contemporary tablets are essentially smartphones in large form factors that offer larger displays. Many tablet models do not include cellular communication but do connect to Wi-Fi.
Today, mobile computing architecture is increasingly cloud-centric, with web and cloud-based access essential for many applications. Key cloud computing services include software distribution, device management, data storage and sharing, and access to shared applications.
Mobile computing is expected to play an increasingly important role in people's lives as the use of edge computing, IoT and 5G technologies expands. Mobile computing and distributed computing complement each other, and information systems will become increasingly reliant on both.
One of the challenges of mobile computing is security. Learn about four mobile security threats businesses face.






