Apple
What is Apple?
Apple Inc. (formerly Apple Computer Inc.) is an American computer and consumer electronics company famous for creating the iPhone, iPad and Macintosh computers. Apple is one of the largest companies globally with a market cap of over 2 trillion dollars.
Apple devices are renowned for their design aesthetic and attention to detail. Tight integration between hardware and software gives their systems a performance advantage over competitor systems with similar specifications.
Apple rose to its position as a market leader by correctly positioning its products. They didn't invent personal computers, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), mp3 players, smartphones, smartwatches or tablets. Instead, they produced some of the first versions of these products that were refined, easy to use and well-designed, which led to wide market adoption.
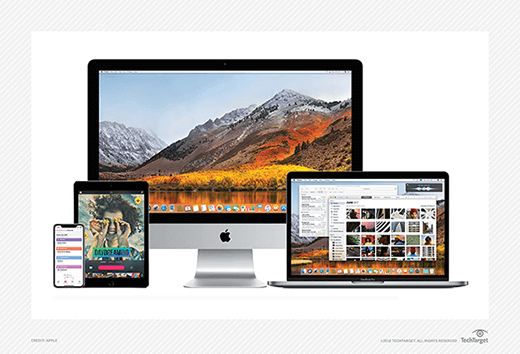
Apple product lines
Apple offers numerous products and services. A few of its major offerings today include:
Mac computer. The Macintosh, or Mac, is Apple's line of personal computers. Its main product types are the iMac all-in-one desktop, Mac mini standard desktop, Mac Studio media-focused desktop, Mac Pro professional production workstation desktop, MacBook Air consumer laptop and MacBook Pro professional laptop.

All Mac computers use the macOS operating system. Since 2020, they use the "M" series CPUs designed by Apple based on ARM architecture. These chips have been praised for their excellent performance and power efficiency. Mac computers are popular with students and creative professionals for their elevated style and ease of use. Computer programmers might also use them because the underlying operating system is based on Unix and is POSIX compatible. Due to the lack of built-in central management and high cost, Mac computers have historically been unpopular in the workplace. Still, the introduction of Zero Trust, BYOD and third-party tools such as Jamf have begun to make them more acceptable to IT administrators.
iPhone and iPad. The iPhone is Apple's smartphone line, and the iPad is its tablet. The iPhone was the first smartphone to receive mass market adoption due to its ease of use, built-in app store and capacitive multitouch touchscreen. The iPhone uses the "A" series mobile CPU, and recent iPads use the same "M" series CPUs as Mac computers. Their operating systems iOS and iPadOS, are based on the same Unix kernel as macOS but have a touch-focused interface.
Apple Watch. The Apple Watch is a smartwatch and fitness tracker. It can monitor health signals, such as ECG, blood oxygen and heart rate data. It can also act as a digital key, allowing users to unlock, lock and start compatible cars. The Apple Watch runs on the watchOS operating system.
Apple TV. Apple TV is a television set-top box and streaming media device. AppleTV has voice control capabilities and can integrate with other Apple devices via Airplay. It also has video conferencing features and the ability to locate the Siri remote. The Apple TV runs on the tvOS operating system.
Apple Airtag. The Apple Airtag is a small tracking device. Users can attach it to items they wish to track and see its location using the Find My app. The Airtag uses Bluetooth to establish its location by communicating with other devices in the Find My network.
Vision Pro. The Apple Vision Pro is a mixed reality headset -- an augmented reality headset also capable of virtual reality. It was debuted at WWDC – Apple's annual developers conference -- in 2023, and it became available in all U.S. Apple Store locations and the Apple Store online on Feb. 2, 2024. It runs on the visionOS operating system, which displays apps using spatial computing. The user interface is controlled by eyes, hands and voice. Users can video conference, stream media and capture images using a three-dimensional camera. The headset has advanced eye tracking and optical identity features – called Optic ID -- for authentication and security. The Vision Pro supports Microsoft Word, Excel and Teams. It is available starting at $3,499, with 256GB of storage. Zeiss optical inserts are also available for this headset, at $99 for readers and $149 for prescriptions.
Services. Apple also provides several services that seamlessly work with its products. Apple iCloud is a personal file storage and synchronization service. Apple Pay is a money payment system and a credit card provider. Apple TV+ is a media streaming service with movies and TV programming. Apple also provides other media under the iTunes store, Apple Music, Apple Books and other services. iMessage is an Apple device-specific instant messaging service that extends SMS for iPhones.
Apple Inc. history
Apple Computer was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak. The third founding member, Ronald Wayne, quickly sold his ownership to Jobs and Wozniak. Their first product was the Apple I microcomputer, which they built in Jobs' family garage. It was sold as a single board with CPU and RAM, but without other basic components such as a keyboard and monitor.
The Apple II was introduced in 1977. It was a commercial success due to its ease of use, color graphics and VisiCalc, a spreadsheet program. Its popularity propelled Apple to become the leading computer manufacturer in America and led to one of the largest IPOs of its time.
Steve Jobs became obsessed with GUIs after seeing Xerox's early Alto system. This led him to add a GUI to the next Apple system, the Apple Lisa. Under Jobs' direction, the Apple Lisa development went far over time and over budget, which led to his being removed as the head of the project. The Apple Lisa was eventually released in 1983 but was a commercial flop due to its high price and lack of software.
Jobs moved to head development of the Macintosh computer. An advertisement heralded its release in 1984 during the Super Bowl with a dystopian 1984 theme, which was a direct challenge to the market leader IBM. This advertisement is widely considered one of the greatest ads ever shown on television. Despite this, the Macintosh had poor initial sales due to its high price and low performance.

The conflict between Steve Jobs and then Apple CEO John Sculley over the release of the Macintosh led to Jobs being removed from all duties by the board of directors. This caused Jobs to leave Apple and start a new company, NeXT computers. At about this time, Steve Wozniak also stepped down from a leadership role at Apple due to personal reasons.
Despite the loss of its founding members, Apple continued to do well in the late 1980s and early 1990s. This was largely due to continuing sales of the Apple II and the eventual success of an upgraded Macintosh in the creative market. During this time, Adobe products, such as Photoshop and Publisher, and other high-quality digital publishing software were only available on Macintosh.
Several factors led to Apple losing profitability, and almost going bankrupt in the mid-1990s. Apple experimented with releasing other consumer electronics products. The most disastrous of which was the Newton tablet. Apple also faced stiff competition from lower-cost Microsoft Windows-based PCs, especially with the release of Windows 95. The Macintosh operating system was also starting to show its age and did not properly support Multitasking.
Desperate to return to profitability and find a new operating system for its computers, Apple purchased Steve Jobs' new company, NeXT in early 1997. Jobs was then named interim CEO of Apple after the former CEO was ousted in mid-1997. He was able to refocus Apple on its core computer business and save it from bankruptcy. In 1998 the iMac was introduced. It was designed by Jonathan Ive and was popular for its friendly colorful gumdrop shape. Apple also introduced video editing and CD/DVD mastering software, cementing Macintosh's role in digital media production.
Mac OS X was released in 2001. It was based on the operating system work of NeXT and used the stable and secure BSD Unix kernel. Also, in 2001, Apple released the iPod to wide acclaim, establishing Apple's place as a trendsetter in consumer electronics.
The iPhone was introduced in 2007, becoming one of the first popular smartphones. The next year App Store launched, allowing third-party developers to sell and market their apps to users. The iPhone was followed by the popular iPhone 4 and iPad in 2010.

In early 2011 Steve Jobs took a leave of absence; naming Tim Cook as the new CEO of Apple. Steve Jobs died on October 5, 2011.
Apple has continued to release new products and expanded services in recent years. Apple has switched to using its own in-house designed CPUs, first in iPhone and now in its Macintosh line of computers. It also offers media streaming services through Apple TV+ and Apple Music. It is expected that Apple might enter new markets soon, with rumors that a virtual reality/augmented reality headset and a self-driving automobile in development.
See how Apple Mac performance and features boost its appeal to business and explore what role Apple TV can serve within a business. Learn how to support Mac computers in Windows environments and check out a guide to enrolling Apple devices in Jamf.
