m-commerce (mobile commerce)
What is m-commerce?
M-commerce (mobile commerce) is the buying and selling of goods and services through wireless handheld devices such as smartphones and tablets. M-commerce is a form of e-commerce that enables users to access online shopping platforms without the use of a desktop computer.
Over time, content delivery through wireless devices has become faster, more secure and scalable. As a result, mobile commerce has grown rapidly.
Examples of m-commerce include in-app purchasing; mobile banking virtual marketplace apps, such as the Amazon mobile app; and digital wallets, such as Apple Pay, Google Pay and Samsung Wallet.
Examples of m-commerce use in specific industries include the following:
- Financial services. Mobile banking and brokerage transactions are done from mobile devices.
- Telecommunications. Handheld devices are used to make service changes and bill payments, and to do account reviews.
- Service and retail. Consumers place and pay for orders on-the-fly through online stores.
- Information services. Financial, sports, traffic, weather and many other news updates are accessed through mobile devices.
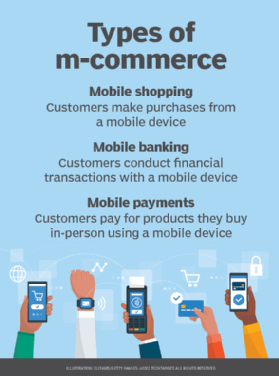
Types of m-commerce
M-commerce is categorized based on the following three basic functions:
- Mobile shopping enables customers to buy a product using a mobile device with an application such as Amazon or a web app. A subcategory of mobile shopping is app commerce, which is a transaction that takes place over a native app.
- Mobile banking is online banking designed for handheld technology. It enables customers to access accounts and brokerage services, conduct financial transactions, pay bills and make stock trades. This is typically done through a secure, dedicated app provided by the banking institution. Mobile banking services may use SMS or chatbots and other conversational app platforms to send out alerts and track account activities. For example, the WhatsApp chatbot lets customers view their account balance, transfer funds, review loans and conduct other transactions in real time through WhatsApp.
- Mobile payments are an alternative to traditional payment methods, such as cash, check, credit and debit cards. They enable users to buy products in person using a mobile device. Digital wallets, such as Apple Pay, let customers buy products without swiping a card or paying with cash. Mobile payment apps, such as PayPal, Venmo and Xoom serve the same purpose and are popular options. Mobile consumers also use QR codes to pay for things on their mobile phones. With mobile payments, users send money directly to the recipient's cell phone number or bank account.
How mobile commerce works
With most m-commerce enabled platforms, the mobile device is connected to a wireless network that is used to conduct online product purchases and other transactions.
For those in charge of developing an m-commerce application, important key performance indicators to monitor include the following:
- total mobile traffic;
- total application traffic;
- average order value; and
- the value of orders over time.
Similarly, tracking the mobile add-to-cart rate will help developers see if users are becoming customers. M-commerce developers may also be interested in logging average page loading times, mobile cart conversion rates and SMS subscriptions.
Mobile payment products operate through a form of peer-to-peer sharing. Once a mobile device is paired with a user's bank card information, the phone can be waved over a payment terminal to pay for a product. Contactless payment using a mobile device uses near-field communication technology.
M-commerce vs. e-commerce
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce refers to buying and selling goods and services over the internet. E-commerce and m-commerce are similar, but they come with a few distinctions from each other, such as the following:
Mobility. E-commerce transactions can be conducted through a desktop computer where the user is in a fixed spot. This reduces mobility as it can be difficult to move around a desktop device. M-commerce offers greater mobility as it's conducted through handheld devices that can be used anywhere there's an internet connection, including buses, trains and airplanes or when exercising at the gym.
Location tracking. Many e-commerce apps make use of location tracking capabilities to pitch users opportunities based on their location. However, the location tracking capability of e-commerce is limited when it is used with a nonmobile device. For example, the location of an e-commerce shopper is tracked with their IP address. While the IP address provides a broad region of the user's location, it is not capable of identifying the exact location, which might affect the targeted advertising strategies of a business. M-commerce apps, on the other hand, can track locations using Wi-Fi and GPS-based technologies that enable location-specific content and personalized recommendations. For instance, a provider can send push notifications offering personalized discounts that target certain customers as they walk past a specific store in a mall.
Security. Credit cards are still commonly used for nonmobile e-commerce payments. They are considered riskier than other online payment methods, even with security measures, such as multifactor authentication. Most data breaches and identity thefts happen because of credit card misuse. M-commerce closes some security gaps through the addition of measures such as biometric authentication, mobile wallets, quick response or QR codes and even cryptocurrencies.
Reachability and convenience. M-commerce makes it easier to reach a target audience. With mobile apps, businesses can reach more people and make their buying experience easier and faster.
Advantages and disadvantages of mobile commerce
The advantages of m-commerce include the following:
- Large customer base. M-commerce provides for a larger customer base and better retention than e-commerce in general, because m-commerce capabilities are more widely and easily accessible. Also, mobile analytics offers insights into customer shopping behavior, pattern and history. To boost retention rates, businesses can use this data to target shoppers with personalized offers and tailor-made discounts.
- Convenience. M-commerce makes it easier for customers to compare prices, read reviews and make purchases when and where they want to do these things.
- Product variety. Customers can browse through a huge inventory of products while also taking advantage of the competitive pricing.
- Automation. M-commerce automates a business's point of customer contact and sales with a variety of mobile contactless payment options, such as Apple Pay, PayPal One Touch and Visa Checkout. Many e-commerce sites also offer one-click checkout process functionality, which enables users to add payment information only once and then use the one-click option for every purchase made thereafter.
- Omnichannel experience. M-commerce creates an omnichannel experience where products can be sold via multiple channels -- e-commerce websites, Amazon, eBay, Instagram. This approach makes it easier for customers to buy whenever and wherever they want.
Disadvantages of m-commerce include the following:
- Poor execution. The smaller screens of mobile phones and tablets require specific navigation functionality. Consequently, intuitive mobile user interfaces are complicated and expensive to design. A poorly executed mobile customer experience can frustrate customers and deter them from making purchases.
- Payment issues. Mobile payment options are not available in every geographic location and may not support every type of digital wallet.
- Tax compliance. Businesses must know and comply with tax laws and regulations of all countries they ship to. Some businesses will avoid this by only authorizing purchases from and shipping to their country of origin.
- Security vulnerabilities. Many users are still hesitant to make purchases over a mobile device because of security risks. Even with two-factor authentication, mobile fraud is on the rise and many merchants have still not adopted fraud prevention practices for the smaller screen. Attacks, such as SIM swaps and mobile malware, are becoming more common and can discourage users from making payments through their mobile devices.
Future of mobile commerce
Mobile commerce is evolving and starting to reach a wider audience. According to Insider Intelligence, 6.9% of retail transactions will take place through a mobile device in 2022 and m-commerce will account for 10.4% of all retail sales by 2025. Many businesses are adopting mobile commerce to avoid falling behind the competitors.
The following are some of the current and future mobile commerce trends:
Mobile retargeting. This concept is an extension of location-based mobile marketing. Instead of putting ads at random places, this trend targets them contextually only at potential customers. For example, marketers can send an ad to users who have previously visited their mobile app or they might present an active mobile targeted ad to a user who comes into proximity of their store. Mobile retargeting offers a better return on investment compared with other advertisement strategies and is likely to become more popular in the future.
Augmented reality (AR). The number of mobile applications with embedded AR is growing rapidly. To improve its brand presence and provide digital content optimization, retail giant Ikea introduced an AR mobile application in 2017 that lets shoppers test products in real time through Apple iOS 11's ARKit technology. Customers use AR models of IKEA furniture from the mobile app to see how those pieces fit in their home and office spaces. Many brands, including Coca-Cola, Zara, Covergirl and Pez, also use embedded AR in their mobile apps.
Mobile SEO. With the growing number of smartphone users accessing the internet, mobile responsive websites have become a necessity. Websites that are not mobile-friendly or do not provide a good user experience risk user abandonment, which in turn increases the bounce rate of their websites. Websites with higher bounce rates rank lower in SEO and Google searches. Therefore, building mobile websites that are adaptive to handheld devices is an important goal for all businesses.
Mobile banking. The biggest advantage of mobile banking is the ability to send money anywhere, anytime. Users can send money to others and conduct transactions with their bank irrespective of their location. This trend is likely to keep growing. According to Business Insider, as of 2021, there are an estimated 169.3 million mobile banking users in the United States, of whom nearly 80% said that mobile banking was their preferred way to access their accounts.
AI, chatbots and shopping assistants. Powered by AI, chatbots are becoming essential e-commerce tools. They help shoppers around the clock with product recommendations, purchase completion, customer support and other tasks. According to a Grand View Research report, the global AI chatbot market is expected to reach $3.99 billion by 2030. Shoppers are becoming more comfortable with chatbots as they have become accustomed to chatting with their friends and family over chat apps, such as WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger and Telegram.
Mobile ticketing. Gone are the days when users had to wait in long lines to buy movie or concert tickets. With mobile ticketing, users can buy and receive tickets through their smartphones. Mobile ticketing also eliminates the need to print the tickets as users receive them on their phones in a text format with a barcode that gets scanned at events.
With mobile commerce on the rise, mobile apps are a necessity for businesses looking to build a loyal customer base. Read on to explore the various benefits of investing in a mobile business app.







